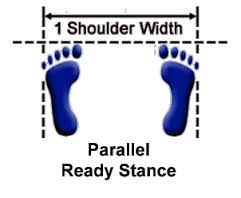
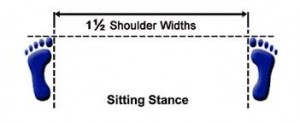
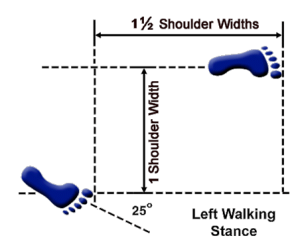
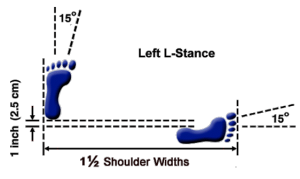
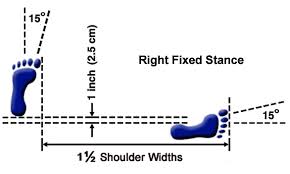
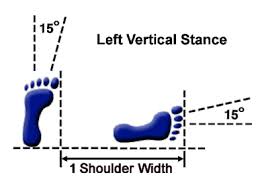
Vertical Stance-Soo Jik Sogi
- The stance has the heel of the rear foot slightly beyond the heel of the front foot and therefore has no width
- It is one 1 shoulder width long, measured from the big toes of the rear foot to the big toe of the front foot
- The weight is distributed 60% on the rear foot and 40% on the front foot.
- Both feet are turned inwards by 15 degrees Both legs are straight.
- This stance determined by the rear foot, and is always performed half facing.
X’ Stance-(Gyocha Sogi)
It has two significant variations, both of which cross the feet over in some way. Variation one is used for landing distance or height jumps, such as in patterns Yul-gok and Toi-gye. Though variation two is used for stepping sideways in a defensive position, such as in pattern Po-eun.
VARIATION 1
The forward foot points outwards from the forward line, and the back foot is behind it on the ball of the foot. Both knees are bent and the back knee leans into the front knee. The weight distribution is mostly on the forward leg. In jumping, the forward leg of this stance is the leg that moves first.